| Contents |
Other Manual Pages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
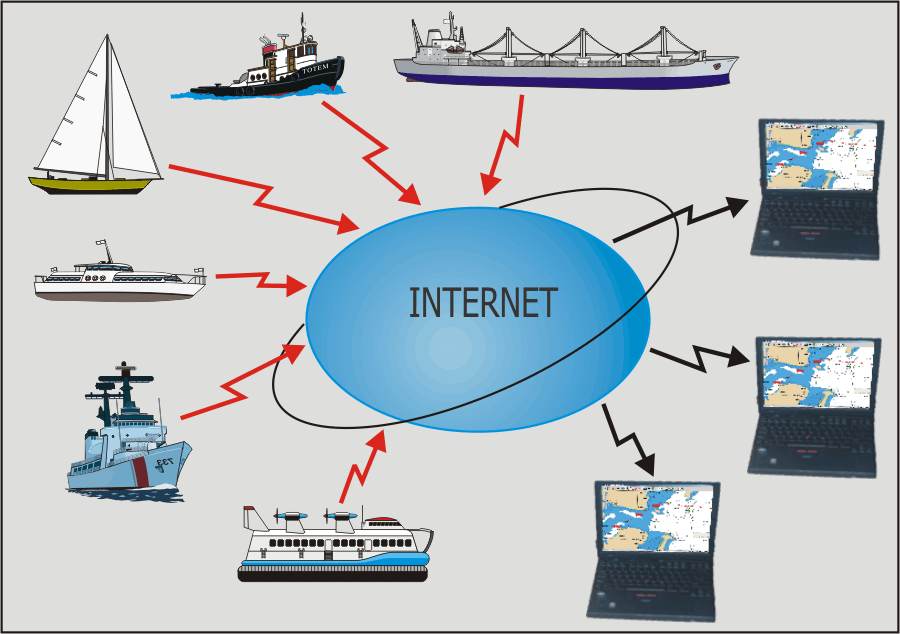
SOB Networking Introduction
Throughout this document, when referring to a
network, we regard this as meaning equally a local network, Intranet,
Internet, VPN, LAN, WAN, Mesh etc etc. Basically any computers linked to each
other and using the Internet standard TCP/IP method for communication.
SOB can operate in two fundamentally
different networking modes - CLIENT and/or SERVER (aka Host & Remote).
SERVER mode will send all NMEA data
received in SOB over the network to any computer that creates a network
"channel" to SOB running in SERVER mode.
CLIENT mode is when SOB is connected
to a remote NMEA data source (either another computer running SOB Server, or
any other commercial or private networked NMEA source).
The remainder of this document discusses use
of SOB in CLIENT mode. Refer to these release notes for use of SOB Server: Release
Notes for SOBvMAXv6 Update
SOB CLIENT can use NMEA data from a remote source
over a network link, either a boat-wide intranet, or the World-wide Internet.
Multiple simultaneous remote connections are
possible.
The number of simultaneous connections is limited only by available
RAM memory and CPU processing speed, and the capabilities of the connecting
hardware. |
 |
| Click the
image for larger display |
There are two key ways to utilise the
networking capabilities of SOB:
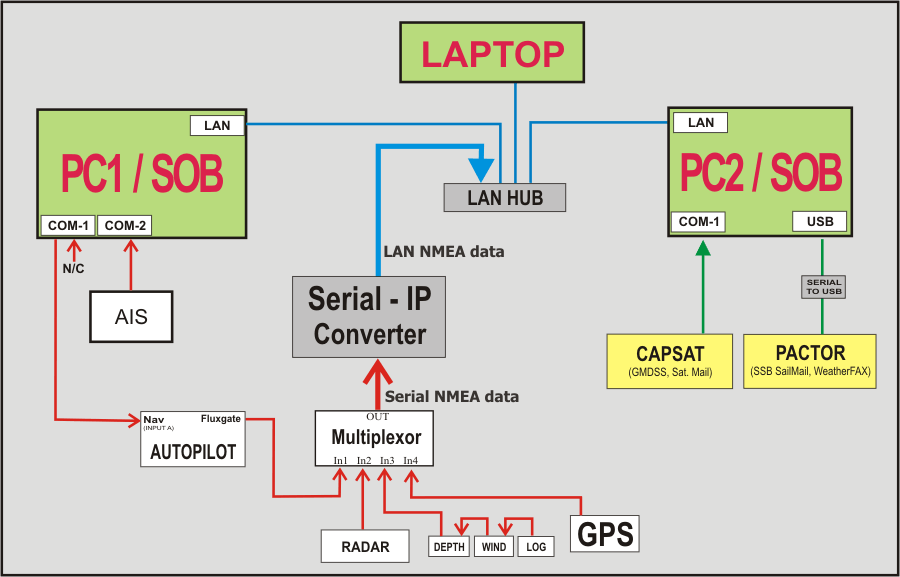
Scenario 1: connect multiple onboard computers
to a
single set of navigation instruments |
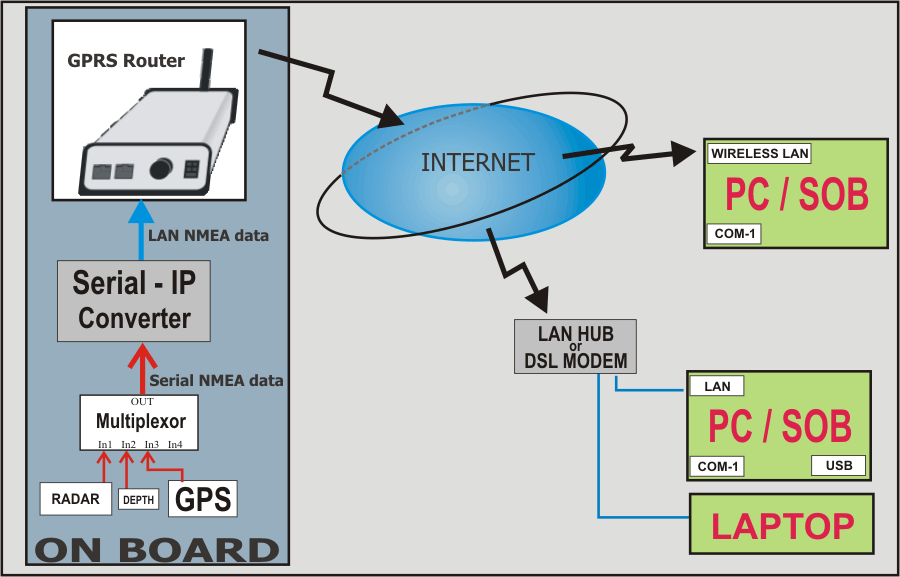
Scenario 2: connect one or more internet enabled
ships to SOB in a remote location |
 |
 |
| Click
an image for larger display |
Any one of the remotely connected ships can be
nominated as Primary and all incoming commands from its URL will drive
SOB in the same manner as would directly connected devices (GPS, depth
sounder, Wind etc). All other remote connections will be represented in SOB as
Targets (using the AIS and ARPA target features of SOB).
Note: AccessLevel 4 is
required for WAN features to be enabled. This a paid SOB upgrade,
refer to the Shop
webpage for ordering details.
Example SOB /
WAN Uses
- Connecting onboard NMEA instruments that
are a long way from the nav computer (Cat-5 or wireless connections are
possible)
- Connecting onboard instruments to multiple
onboard computers
- Use a wireless tablet computer onboard to
navigate your boat
- Monitor your boat, or fleet of boats, from
your desk or home in real-time
- Track a yacht race in real-time from
anywhere in the World

Glossary
| OwnShip |
A reference to a boat
you are onboard (truly or virtually) and running SOB |
|
pictures showing real
and virtual OwnShip scenarios are coming soon ...
|
| TCP/IP |
Transport Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol |
|
The set of standards
that define how data is transported over a network, either a local
network, or the Internet.
|
IP Address
or
URL |
Universal Resource
Locator |
| A unique number or label
that defines a node on a network. Every device connected to an intranet
or Internet has a unique address. The address is in the popular URL
format (eg: www.microsoft.com) or in the "dotted decimal"
equivalent (eg: 127.0.0.1).
|
| WAN |
Wide Area Network |
|
Any network connection,
usually reserved to mean a connection over the Internet. |
| LAN |
Local Area Network |
|
Generally refers to a local
connection, or intranet, such as a home/office network, or a network on
your boat connecting TCP/IP enabled devices.
|
| Intranet |
A network that is self
contained in a single location. Traditionally referred to a network (or
LAN) that was all physically wired together, however the introduction of
wireless connection types (WiFi, Bluetooth etc), has blurred this
definition somewhat! |
| Internet |
Q.E.D.
|
| GPRS |
General Packet Radio
Service |
|
A data communication system
for Internet connection using the GSM wireless mobile cellular phone
network. |
| GPRS Router |
The hardware device
required to connect to the Internet using GPRS. (Basically just a mobile
phone that has a full-time internet connection and only sends data).Each
connected Router is assigned its own IP Address (or URL) so it can be
identified over the Internet, and SOB uses this known IP Address to
establish a one-to-one connection with your boat.
|
| Serial to IP |
Converter or Server |
|
|
A hardware device for
converting serial (COM) data (such as generated by NMEA navigation
devices) to TCP/IP data in preparation for transmission over a network
(intranet or Internet).
|
| Multiplexer |
A hardware device for
combining many NMEA serial devices into a single stream of NMEA data.
|
| NMEA |
National Marine
Electronics Association |
|
A set of international
standards for interfacing marine electronics devices. |
| NEMA |
A typographical error which
should be read as NMEA. |
|
|

|
|
|
|
The WAN
Connect Form
 |
The WAN Connect
button is located on the Raw NMEA Data form. Press the button
to open the WAN Target List form to maintain your connection
list and to connect to the remote targets.
Note: AccessLevel 4 is
required for WAN features to be enabled. This a paid SOB upgrade,
refer to the Shop
webpage for ordering details. |
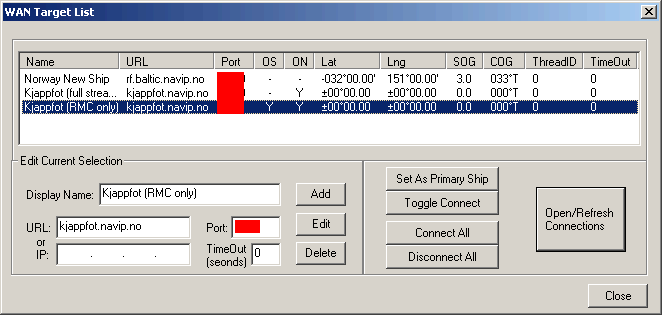
NOTE: The port numbers are
blanked-out in this example to prevent everyone from using these real
connections!
Steps
for connecting to WAN/LAN ship(s) Note:
this applies to a connection over the Internet OR to the devices
on your own ship.
-
Start SOB
>> Open Raw NMEA Data form (double-click chart surface, or
press [N])
>> Press the [WAN Connect]* button.
* if this button is disabled, then
you will need to purchase an AccessLevel 4 UnlockCode, refer to the
Shop webpage.
-
(optional) Make a new
connection:
>> enter a Display Name to help identify the ship (the [Add]
button will then be enabled)
>> enter a URL or IP Address (if an IP Address is
entered, then it will be used instead of the URL) for the remote node.
This URL will be assigned by your network hardware
administrator/installer, or your Internet Service Provider (ISP) of your
GPRS connection
>> the correct Port number that the node's URL uses to
provide a data "path" to the Internet. This will be assigned
with the URL.
>> the TimeOut value in seconds. A default of 10 seconds will
be used if set to 0 or if bigger than 600. The ideal value
will be dependent on the transmission rate configured for your Serial
IP Server to forward its NMEA data to the Internet, and to the
transmission rate of the connected NMEA instruments.
Press [Add] to add the new connection to the list.
-
Select an entry in the list
that you wish to connect to. (Multiple entries can be selected by using
standard Windows™ highlighting commands - eg: hold down Shift and/or
Ctrl keys while selecting to extend the items highlighted)
>> Press the [Toggle Connect]
button. The ON column will display a "Y" for the selected
ship(s).
-
Select [Set as Primary
Ship] if necessary... (refer to scenarios at the top of this section)
Scenario 1: required
Scenario 2: optional
Press this button if you want this ship to display in SOB as the OwnShip.
If not set to OwnShip, the connected boat will be represented in SOB as a
simulated AIS Target.
Notes:
* The OS column will display a "Y" for the connection
that will be used as OwnShip.
* Only one remote ship can be set as OwnShip.
* The OwnShip status can be changed using this form at any time, even when
multiple remote ships are already connected.
* If a connection is changed from not being the OwnShip, to OwnShip, then
its AIS Target symbol will still be on the screen. This can be deleted or
hidden using the Targets form (press [T]) if desired.
* When a remote ship is set to OwnShip, SOB will close any serial (COM)
port currently in use by direct connected GPS (or other instruments), and
the OwnShip remote ship data will be used as the primary NMEA data source
for SOB.
-
Press [Open/Refresh
Connection] button. This button will only be enabled when there are
connections that need to be changed (either opened or closed). After
pressing the button, a message box showing a summary of connections will
be displayed. Press [Yes] to continue.
When a connection is made, a unique number will be entered into the ID
column of the list. This number is used to represent the remote ship
simulated AIS Target. Messages about the connection and disconnection
process are posted to the Messages ViewPanel.
Simulated remote Target MMSI: The MMSI number (which is the unique
AIS number for every ship in the World) is created from the SOB ID number
and is equal to: ID x 10,000.
ARPA Target Note: If the remote ship is also sending ARPA target
NMEA sentences, then these will also appear in the Target list as their
own target, and the MMSI number created for them will be: ID x 10,000 +
(ARPA number). The ARPA number is designated by the remote ship's
RADAR unit and is a number from 01 to 99.
AIS Target Note: If the remote ship is also sending AIS target NMEA
sentences, then these targets will be included in the Target list as if
they were acquired locally (ie: as regular AIS targets). Note: that
potential problems exist if a single SOB session is connected to multiple
remote ships, and its own local AIS receiver, in that the data received
for the SAME target could be received out of synch from all the sources.
The resultant SOB display would show this as the AIS target jumping back
and forward along its track.
Steps
for Disconnecting from a WAN/LAN ship(s)
-
Open the WAN Target List
form, and highlight the entry you wish to disconnect. Any connected ship
will show BOTH a "Y" in the ON column, and a number in
the ID column.
-
Press the [Toggle Connect]
button. The "Y" will be replaced with a "-" in the ON
column, and the [Open/Refresh Connection] button will be enabled.
Several ships can be Disconnected at the same time by repeating these
steps for any other connected ship. ALL currently connected ships can be
flagged for disconnection by pressing the [Disconnect All] button.
-
Press the [Open/Refresh
Connection] button to display a summary of connections to open/close
and continue when ready ...
Using
both IP and Serial devices on OwnShip
When a WAN connection is made,
SOB automatically closes any open serial ports for any direct connected
devices (eg: GPS). This is a safety feature to prevent any misunderstanding
about what data source is being displayed by SOB. When WAN/LAN data is being
displayed as OwnShip data, the Ship's Data ViewPanel will be displayed
with a silver/grey background (see sample Ship's Data displays below).
It is possible, and reasonable,
to use data from both IP and serial connections simultaneously. For instance,
a set of NMEA devices could be located in a remote area of the ship (eg:
rudder angle sensor, GPS antenna, SONAR transducer, fluxgate compass),
combined (using a multiplexer for example) into a single data stream, then run
through a Serial IP Server. The output from the Serial IP Server can then be
transferred to the navigation computer running SOB via Cat-5 LAN cable, or via
a WiFi wireless connection, and connected to SOB as a WAN Connect using
the IP Address of the Serial IP Server.
At the same time, other NMEA devices closely situated to the navigation
computer (eg: RADAR, wind instruments, backup-GPS, AIS Receiver) can be
directly connected to the computer via the normal serial (COM) port(s).
SOB will thus merge data from
the two built-in serial ports, and any ONE connected remote node that is set
as the Primary ship on the WAN Target List form.
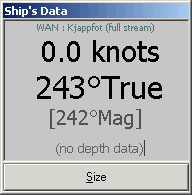
| Ship's
Data ViewPanel display options |
Source:
WAN Connected and set as Primary Ship
 |
Source:
direct Serial (COM) connected GPS and Depth
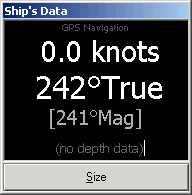 |
Source:
Primary connection doesn't have valid GPS data
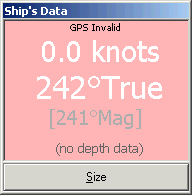 |
| |
Source:
SOB DeadReckoning mode is set, overriding all other data sources
 |
Source:
SOB logfile replay, overriding other connected data sources
 |
|

|








